A company that specializes in managing accommodations for area visitors is now overseeing two additional downtown properties.
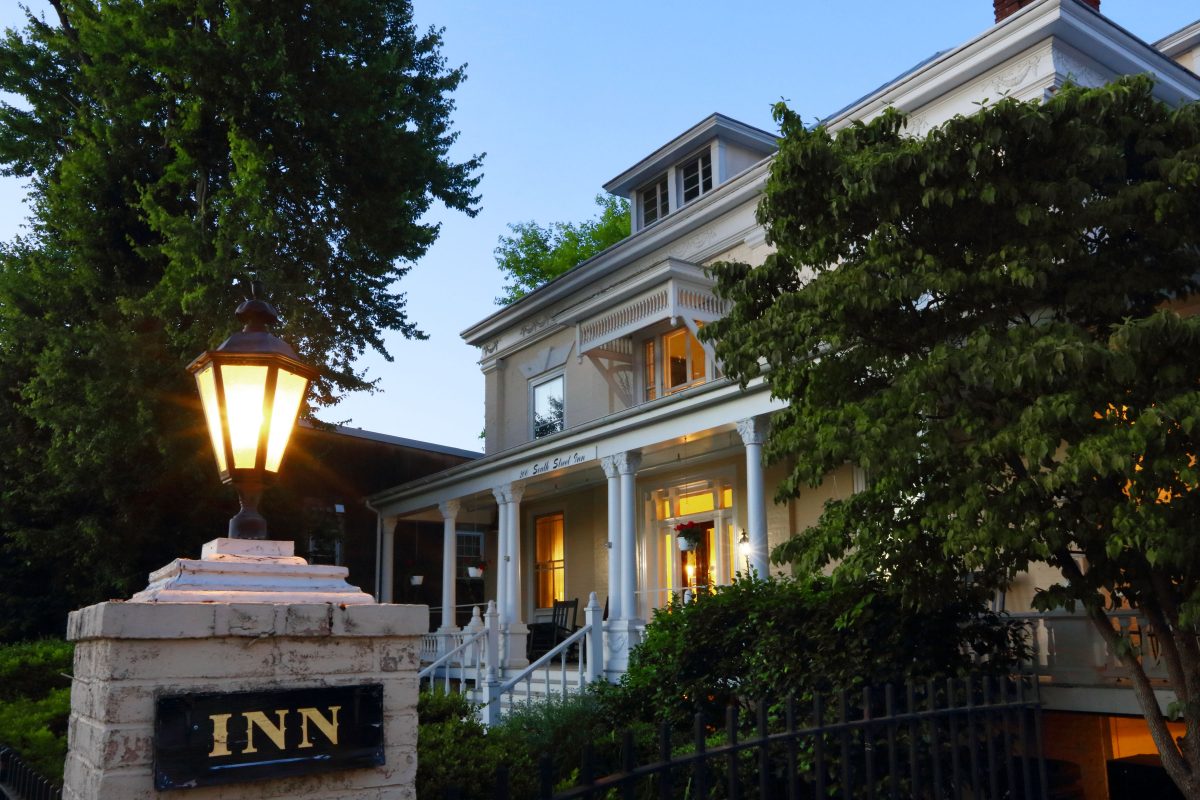
Stay Charlottesville now operates a six-room inn at 400 W. High St. as well as the 200 South Street Inn.
“What’s happening is these really great properties need updating and they had huge amounts of cost associated with them over the last couple of years that drove them to be not successful, so the model needed to change,” says M. Travis Wilburn, one of Stay Charlottesville’s founders.
Wilburn started the company in 2010 when he built a guesthouse on his property that was originally intended for an aging relative. He began renting it out on a short-term basis and created the business to help others manage rental properties to earn extra income. Since then he’s created the Charlottesville Insider website to promote the area as a destination.
“Our group is able to oversee these hotels and be able to drive more direct traffic,” Wilburn says.
While reservations are being taken now at 400 West High, 200 South Street Inn is closed until the spring for renovations.
“Our revitalized vision will keep everything you love about 200 South Street Inn while enhancing it with modern amenities and fresh experiences, like an outdoor pool,” reads the website.
Charlottesville’s Department of Neighborhood Development Services staff are currently processing the application to build that pool.
An LLC called Renaissance Investment purchased the two properties that make up the South Street Inn for $3.46 million in December. A separate entity called 400 West High Street LLC bought the property with that address in June for $1.41 million.
The Inn at 400 West High was established in 2011, but closed last year. The South Street Inn has been in business since 1986 and had been operated by Brendan Clancy since 1991.
Area occupancy rates remain steady, according to data compiled by the Charlottesville Albemarle Convention & Visitors Bureau. October of 2024 was the busiest in recent history, with nearly 80 percent of area rooms booked.
Wilburn says there’s been an increase in the volume of area lodging, and both of these inns will be marketed to groups that can take over the entire property for special events.
“I think they are one-of–a-kind unique opportunities to be able to stay as a family or as a group in these really awesome properties close to downtown and have it just be your own private party,” Wilburn says. “That is not an opportunity that is easy to find.”
The city collected $8.12 million from the lodging tax in FY2023, a rebound from the $3.8 million collected during the pandemic-constrained FY2021. Last spring, council raised the lodging tax rate from 8 percent to 9 percent and budget staff anticipate bringing in $9.56 million in the current fiscal year.
Wilburn says this is paid by people from outside the community, providing valuable revenue for the city.
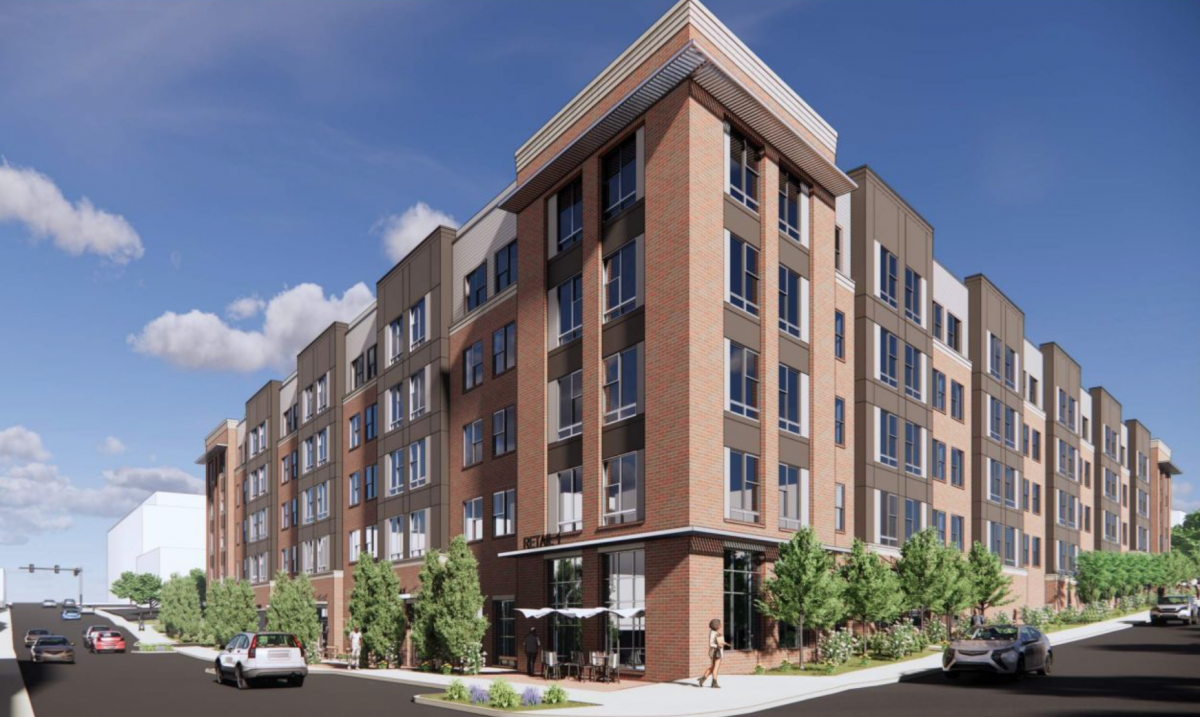
Later this year, the Virginia Guesthouse will open in the University of Virginia’s Emmet-Ivy Corridor with 214 rooms and nine suites. Developer Jeffrey Levien continues work on building a Marriott hotel at 218 W. Market St. There’s still no sign of movement on what will happen with the skeleton of the unfinished Dewberry Hotel.